To be completed by 3/9/2005
Practical Exercises
To practice with Samba server, you need to have Windows installed on
your desktop, and Samba server installed and configured on your
rack-mounted node. Throughout the discussion below, I nominate the
desktop and node as unisys02 and node02. You need to change their names
for that of your computers, accordingly.
A) Dual-boot Linux and Windows 2000 installation on your desktop
1. Archive some system and configuration file on your desktop and scp
them to the node:
2. Run semi-automatic Linux installation like in Lesson #2.
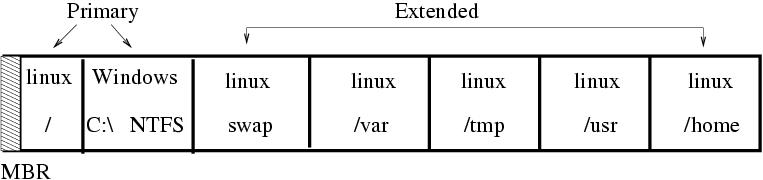
File preseed.cfg implies creating two primary partitions -
one for Linux root (/dev/hda1) and one for Windows (1.5 GB
/dev/hda2)
Hard drive partitions will be set as follows:
 |
3. Boot into Linux.
Install module-init-tools in order to be able to work with
the Kernel-2.6 modules:
Install dosfstools
Create a GRUB boot floppy: put a new floppy in the floppy drive and run
Make sure you can boot the system from the GRUB floppy:
leave the floppy in the drive; reboot the system; at the prompt type
the following:
Make sure " / " partition is located in /dev/hda1 and
install GRUB into the first sector of the root partition:
Create an image of the first sector of /dev/hda1:
dd if=/dev/hda1 of=linux.bin bs=512 count=1;
copy the image onto the same boot floppy:
mcopy linux.bin a:
4. Reboot. Set BIOS to boot from CD-ROM device first.
5. Boot from Windows 2000 installation CD; choose to install Windows 2000 on
the FAT partition and format it as NTFS; Accept this partition as active.
When prompted for computer name during the installation, give the name of
your unisys desktop, for example, unisys02; Check in WORKGROUP.
6. When installation is done, set BIOS back to boot from floppy first.
7. Boot into Windows 2000; start command prompt;
cd C:
copy a:\linux.bin .
edit boot.ini
Add another line in boot.ini:
c:\linux.bin="Linux Debian 3.1"
8. Restart your machine, and you should be able to see two choices appear
on your screen at boot time.
9. To access your cluster node, install SSH client on your Windows desktop,
for example, PuTTY, putty.exe
B) Configuration of Samba server on your cluster node
1. On your cluster node, install Samba packages:
Hit < ESC > during Samba configuration stage.
2. Copy the demo /etc/samba/smb.conf into /etc/samba/smb.conf-original
Configure simple smb.conf file replacing its all original content with
the text below. For Domain Name, pick up
a unique name, for example, your Windows machine name with extension
"DOM", UNISYS02_DOM:
Run the command "testparm" to make sure there is no syntactic errors in smb.conf
3. Create Samba client host trust account on the node for your desktop windows machine.
For example:
groupadd -g 80 trust
useradd -u 80 -g trust -d /dev/null -s /dev/null unisys02$
smbpasswd -a -m unisys02
Add user accounts, for example:
smbpasswd -a root
smbpasswd -a alexei
4. Start Samba daemons, smb and nmb, on the node:
/etc/init.d/samba stop
/etc/init.d/samba start
5. Access Shares on the Windows desktop.
Browsing and accessing the SMB shares from a Windows machine.
On a Windows machine, click on "My Network Places"; click on "entire
contents"; Microsoft Windows Network; choose the Domain you specified in
smb.conf; choose the SMB server; provide user name and password of any
user who has an account in smbpasswd. In the new window, you should see the
home directory content on the SMB server.
Mounting shared drives.
Right click on "My Computer"; choose "Map network drive"; choose
drive letter, for example, F; for the folder, type \\node02\homes;
provide user name and password. You should see a new drive F appeared
in folder My Computer.
Unmounting shared drives.
Right click on "My Computer"; choose "Disconnect Network Drive";
select the Drive to disconnect; OK.
Mounting and Unmounting shared drives can be done through DOS prompt.
To mount share homes from node02:
net use F: \\node02\homes /USER:alexei
To check what shares are mounted:
net use
To unmount the share:
net use F: /delete
6. Binding to the Domain Controller.
Right click on "My Computer"; slide to Properties; choose Network
Identification;
Click on Properties; check-in Member of Domain; type-in the Domain
Name, which you have specified on the Samba server; OK.
When you reboot the machine, you should be able to logon to the
Domain with your user name and password stored on the Samba server.
You home directory would be maped as drive Z. When you logon
to the Domain at first time, Windows creates folder profile in
your home directory.
7. Accessing Windows shares from the Linux node.
Your Samba server can act as an SMB client accessing Windows shares.
For example, create a new folder, C:\shares, on your Windows computer.
Right click on folder shares; choose sharing; check-in Share this folder;
name it "shares"; click on Permissions; Add; in UNISYS** domain put
your login name and password; add also Administrator; click Apply; OK.
Create some text file in folder C:\shares.
Mounting Windows shared drives on Linux:
Check the content of directory /mnt/smb.
Unmount it:
umount /mnt/smb
Mount the directory again accessing it as a Domain user:
mount -t smbfs -o username=alexei,passwd=mypassword //unisys02/shares /mnt/smb
df -h
Then unmount it, umount /mnt/smb
Run SMB client on the Linux machine:
smbclient //unisys02/shares -U "UNISYS02\Administrator"
type-in password
To exit, type "quit" at the prompt:
smb: \> quit
Access it again as a Domain user:
smbclient //unisys02/shares -U alexei
To see the list of the commands, type "help" or "?"
smb: \> help
smb: \> quit
8. Read Chapter 39
Recommended reading: Linux Magazine, Feb. 2002, "Using Samba as a PDC" by Andrew Bartlett